Definition and a Brief History of AI
Any human-like behaviour
that a machine or system exhibits is a demonstration of Artificial Intelligence (AI). In the simplest type of
AI, computers are taught to "imitate" human behaviour utilising a wealth of data from prior instances of the
same activity. This can include everything from identifying the distinctions between a cat and a bird to
carrying out difficult tasks in a manufacturing environment. AI is now a part of our daily life, despite its
early versions enabling computers to compete against people in games like chequers. In addition to solutions for
healthcare, manufacturing, financial services, and entertainment, we also have AI solutions for quality control,
video analytics, speech-to-text, and autonomous driving.
The first attempts to define human thought as a symbolic system by classical thinkers are where modern
Artificial Intelligence (AI) got its start. The phrase "Artificial Intelligence" was first used in a conference
at Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire, in 1956, but the field of AI was not fully established until
later.
The idea of testing a "thinking" machine was put forth in a paper by a man by the name of Alan Turing
in 1950. He thought a computer could be said to be thinking if it could have a conversation using a teleprinter,
resembling a human without any obvious deviations.
Click the button below to view my selected AI technology, Facial
Recognition
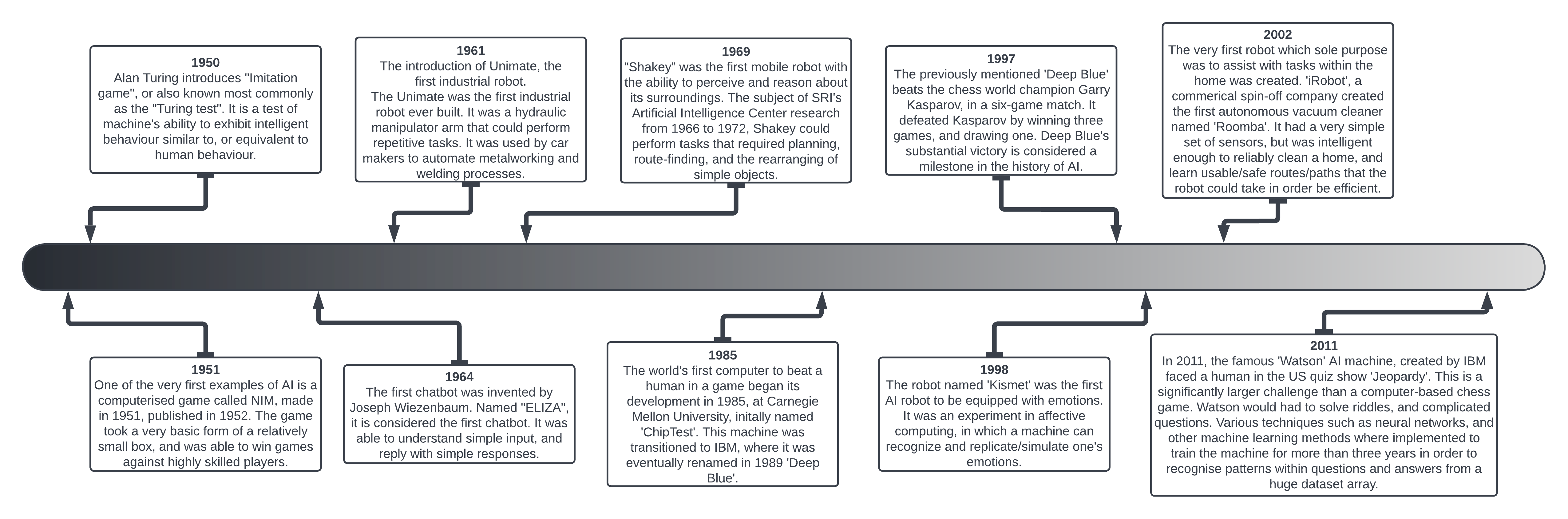
A timeline of Artificial Intelligence, styled & formatted using Lucid.app